JUSTUS2/Visualization: Difference between revisions
K Siegmund (talk | contribs) m (K Siegmund moved page TigerVNC to JUSTUS2/Visualization) |
K Siegmund (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| width=600px class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
! Description !! Content |
|||
|- |
|||
| module load |
|||
| vis/tigervnc |
|||
|- |
|||
| Availability |
|||
| [[bwForCluster_JUSTUS_2]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| License |
|||
| [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_General_Public_License GPL] |
|||
|- |
|||
| Citing |
|||
| n/a |
|||
|- |
|||
| Links |
|||
| [http://www.tigervnc.org/ Homepage] |
|||
|- |
|||
| Graphical Interface |
|||
| No |
|||
|} |
|||
= Description = |
= Description = |
||
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a protocol to use a virtual desktop on a server on your local computer. It allows you to launch and use graphical applications on remote machines. |
|||
users to launch and interact with graphical applications on remote machines. It is usually faster than standard X11 forwarding and thus should |
|||
be used if a graphical software feels slow and has bad responsiveness. |
|||
= Availability = |
|||
TigerVNC is a high-performance implementation of VNC and is installed on JUSTUS2 as the [[Software Module]] vis/tigervnc |
|||
TigerVNC is available on selected bwHPC-Clusters. A complete list of versions currently installed on the bwHPC-Clusters can be obtained from the [https://www.bwhpc.de/software.html our software page]. |
|||
= Overview = |
= Overview = |
||
| Line 43: | Line 19: | ||
First, you have to start the VNC Server on the cluster. The startup procedure depends on the cluster and hardware you are using. |
First, you have to start the VNC Server on the cluster. The startup procedure depends on the cluster and hardware you are using. |
||
<!--* [[VNC Server - bwUniCluster 2.0]]--> |
|||
* [[VNC Server - bwForCluster Chemistry]] |
* [[VNC Server - bwForCluster Chemistry]] |
||
* [[VNC Server - bwForCluster Chemistry - 3D Acceleration]] |
* [[VNC Server - bwForCluster Chemistry - 3D Acceleration]] |
||
Revision as of 15:28, 14 July 2022
Description
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a protocol to use a virtual desktop on a server on your local computer. It allows you to launch and use graphical applications on remote machines.
TigerVNC is a high-performance implementation of VNC and is installed on JUSTUS2 as the Software Module vis/tigervnc
Overview
You will need to do the following steps to use VNC on the cluster:
- start a vnc server on the cluster - This will create a virtual desktop on that node
- make an ssh tunnel to allow outside access for yourself to the server
- use a vnc client on your home desktop to connect to the virtual desktop
- kill the vnc server after you finshed
VNC Server
First, you have to start the VNC Server on the cluster. The startup procedure depends on the cluster and hardware you are using.
The VNC server will open a virtual display with a display number. It will e.g. be called ":01"
Create a Tunnel
- VNC port: The connection port is on 59XX. A display :01 will have port 5901, a display :02 will have port 5902 etc.
The script run_vncserver gives you instructions on how to create the tunnel. It will fill in the correct user name and port for your case.
- Linux/Unix Commandline
ssh -fCL port:localhost:port user@justus2-login03.rz.uni-ulm.de
-f: sends the ssh into the background
-C: compress all data
-L local_port:host:hostport: "local" port forwarding. The port on the remote machine can be accessed on the machine from where you run ssh
If you have to go via more than one linux machine, you can chain several of these ssh tunnels.
- Putty on Windows
Connection -> SSH -> Tunnels
Source Port: 59XX
Destination: justus2-login03.rz.uni-ulm.de:59XX
- TightVNC (Java Client)
This client (and only the Java version of the client!) allows to configure ssh tunneling as part of opening the VNC connection. See description in the following client section
VNC Client
The startup script of the VNC Server should have printed out detailed instructions about how to establish a connection to the VNC Server from your local computer. These instructions depend on the operating system (e.g., Linux/macOS, MS Windows) you are using and if you work with TurboVNC Java Viewer which is a tool that can simplify the handling but needs the Java Development Kit (JDK) to run. Therefore, the next steps are divided into three cases. The commands should be executed on the local computer.
- Login using TurboVNC Java Viewer
Needed software: TurboVNC, JDK
Open the TurboVNC Java Viewer and navigate to Options... -> Security -> Gateway to fill in the parameters provided by the run_vncserver script. You can save these settings in the "Global" tab if you want to. Subsequently, click "OK" and connect to the cluster by supplying the VNC Server as given to you by run_vncserver. Before the connection is established, you should be prompted for your SSH and VNC password, respectively.
- TigerVNCLinux Debian-based
sudo apt install tigervnc-viewerfill in information supplied by run_vncserver, e.g.xtigervncviewer :3
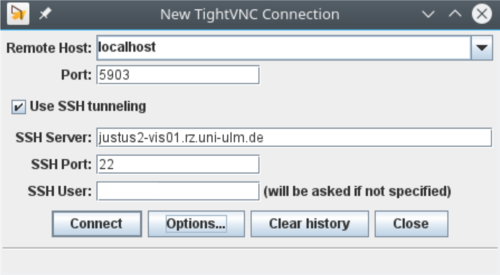
- Login using TightVNC Java Viewer
Needed software: TightVNC
Start the TightVNC Viewer: On Linux, open a terminal and execute the following command:$ java -jar tightvnc-jviewer.jar. On Windows, just double-click tightvnc-jviewer.jar in the Windows Explorer.
Fill in the parameters given to you by the run_vncserver script (see example below), add your username at SSH User, and press connect to establish a VNC session.
- Login without TurboVNC Java Viewer for Linux users
Needed software: A VNC Client such as TurboVNC
A SSH tunnel must be created with the command given to you by the run_vncserver script, e.g.:$ ssh -fCL 5903:localhost:5903 <UserID>@justus2-vis01.rz.uni-ulm.de
Start your VNC Client and connect to localhost:n, where n is the display number, using the command given to you by the run_vncserver script. E.g.:$ vncviewer localhost:3
- Login without TurboVNC Java Viewer for Windows users
Needed software: TigerVNC, Putty
Start Putty and navigate to Connection -> SSH -> Tunnels to fill in the parameters provided by the run_vncserver script. Subsequently, clicked "Add" and navigate to Session to connect with the cluster using your username and password. Once the connection is established, start the TigerVNC Client and connect to localhost:n, where n is the display number provided by run_vncserver.
Shutdown your VNC session
To exit your VNC session it is not sufficient to only close the VNC viewer, since this will not terminate the VNC Server. The VNC Server will keep running and you will run into problems when you try to start a new VNC session later on. Please use the "log out" function of the desktop environment inside the VNC session, this will terminate the VNC server properly. Alternatively, you can terminate the VNC Server on the compute cluster using
$ vncserver -kill :n
with n specifying the display number.
OpenGL applications within VNC sessions
Executing an OpenGL program during a 3D accelerated VNC session will issue an error. In order to fix this, open a terminal window and run your application through the VirtualGL wrapper using the vglrun command like in the following example for the benchmark application glxgears:
$ vglrun glxgears -info