Registration/SSH
SSH Key Authentication for HPC Clusters
SSH Keys allow you to log into a system without entering a password. Instead of proving your identity with something you know (a password), you prove it with something you have (a cryptographic key).
| Cluster | Management Method | Details |
|---|---|---|
| bwUniCluster 3.0 | bwIDM Portal | Centralized key management, 180-day validity |
| bwForCluster BinAC 2 | ~/.ssh/authorized_keys | Self-managed, use ssh-copy-id |
| bwForCluster Helix | bwServices Portal | Centralized key management, 180-day validity |
| bwForCluster JUSTUS 2 | ~/.ssh/authorized_keys | Self-managed, use ssh-copy-id |
| bwForCluster NEMO 2 | bwIDM Portal | Centralized key management, 180-day validity |
Choose your cluster below:
- BinAC 2 and JUSTUS 2 - Self-managed keys
- bwUniCluster 3.0, Helix, and NEMO 2 - Centralized management
SSH Keys on BinAC 2 and JUSTUS 2
On bwForCluster BinAC 2 and bwForCluster JUSTUS 2, you manage SSH keys yourself using the standard ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
Quick Setup with ssh-copy-id
The easiest method to add your SSH key:
Step 1: Generate an SSH key (if you don't have one):
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
Press Enter to accept the default location, then set a strong passphrase.
Step 2: Copy your key to the cluster:
# For BinAC2: ssh-copy-id username@login.binac2.uni-tuebingen.de # For JUSTUS2: ssh-copy-id username@justus2.uni-ulm.de
Enter your service password and OTP when prompted. Your public key will be automatically added to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys.
Step 3: Test your connection:
# For BinAC2: ssh username@login.binac2.uni-tuebingen.de # For JUSTUS2: ssh username@justus2.uni-ulm.de
You should now be able to log in using your SSH key and OTP.
Manual Setup (Alternative)
If ssh-copy-id is not available on your system:
Step 1: Display your public key:
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
Copy the entire output.
Step 2: Log into the cluster using your service password and OTP
Step 3: Add the key to authorized_keys:
mkdir -p ~/.ssh chmod 700 ~/.ssh echo "paste-your-public-key-here" >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Replace paste-your-public-key-here with your actual public key.
SSH Keys via bwIDM/bwServices
On bwUniCluster 3.0, bwForCluster Helix, and bwForCluster NEMO 2, SSH keys are managed centrally through the registration service.
Why Centralized Management?
Centralized SSH key management provides:
- Security enforcement: Keys must use strong algorithms and have 180-day validity
- Centralized control: Review and revoke all keys from one location
- Two key types: Interactive keys (manual logins) and Command keys (automated workflows)
Note: Self-managed ~/.ssh/authorized_keys files are ignored on these clusters.
Supported Key Types
Standard SSH Keys
- ED25519: 256 bits (recommended)
- RSA: 2048 bits or more
- ECDSA: 521 bits
Important: Always protect your private keys with a strong passphrase.
FIDO2 Hardware Keys
ED25519-SK keys use hardware security keys (like Yubikey) for authentication:
- Always valid - no 2-factor unlock required
- Hardware-protected - private key never leaves the device
- Physical presence required - must touch key to authenticate
Note: ECDSA-SK keys are not supported. Use ED25519-SK only.
| Cluster | ED25519-SK Support |
|---|---|
| bwUniCluster 3.0 | ✓ Supported |
| bwForCluster Helix | ✗ Not supported |
| bwForCluster NEMO 2 | ✓ Supported |
Get started: See SSH with Yubikey - Quick Start Guide
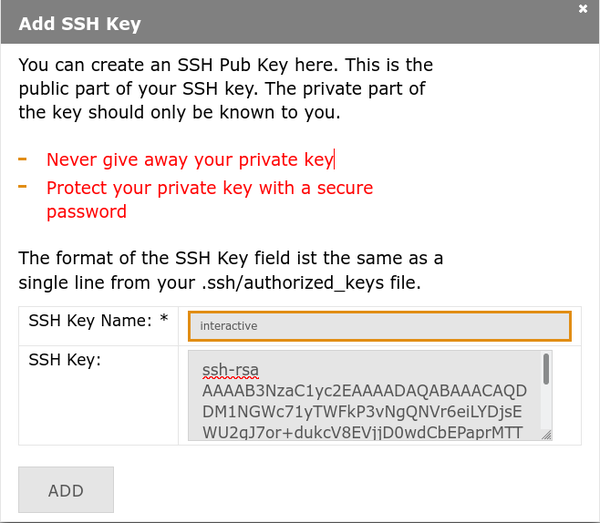
Step 1: Add Your SSH Key to the Portal
First, upload your public key to the management portal:
Important:
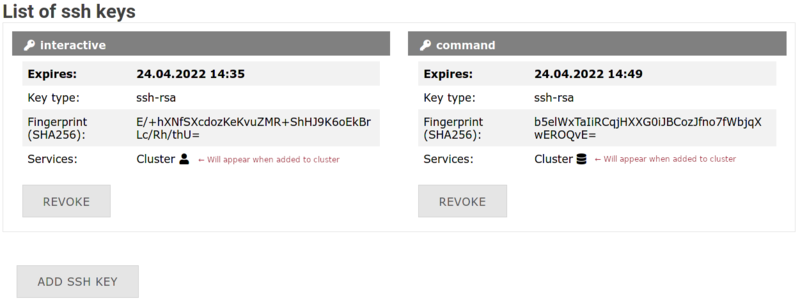
- Keys are valid for 180 days and automatically revoked after expiration
- Upload only your public key file (ending in
.pub, e.g.,~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub)
1. Navigate to SSH key management:
- bwUniCluster 3.0 / NEMO 2 (bwIDM)
- bwForCluster Helix (bwServices)
2. Click "Add SSH Key" / "SSH Key Hochladen"
3. Enter key details:
- Name: Descriptive identifier (e.g., "laptop-work", "desktop-home")
- SSH Key: Paste complete contents of your
.pubfile - Click Add / Hinzufügen
4. Success! Your key appears in the list
Next: Bind your key to a cluster as either an Interactive Key or Command Key.
Step 2A: Register Interactive Key
Interactive Keys are for manual SSH logins.
Understanding Key Validity
Regular SSH Keys (RSA, ECDSA, ED25519):
- Require 2-factor authentication unlock
- Valid for limited hours after entering OTP + service password
- Must re-authenticate when validity expires
| Cluster | Valid Duration |
|---|---|
| bwUniCluster 3.0 | 8 hours |
| bwForCluster Helix | 12 hours |
| bwForCluster NEMO 2 | 12 hours |
FIDO2 Hardware Keys (ED25519-SK):
- Always valid - no 2-factor unlock needed
- Authentication via physical key touch only
- Only on bwUniCluster 3.0 and NEMO 2 (not Helix)
- See Yubikey Quick Start Guide
Registration Steps
1. Add your public key following Step 1 above
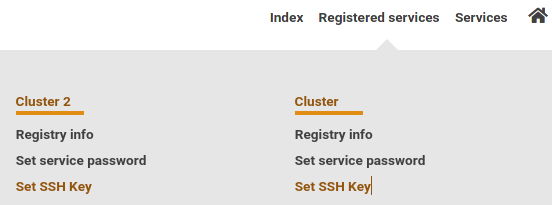
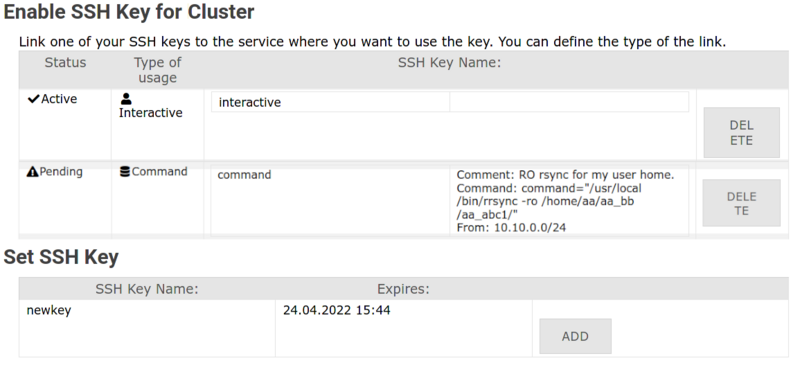
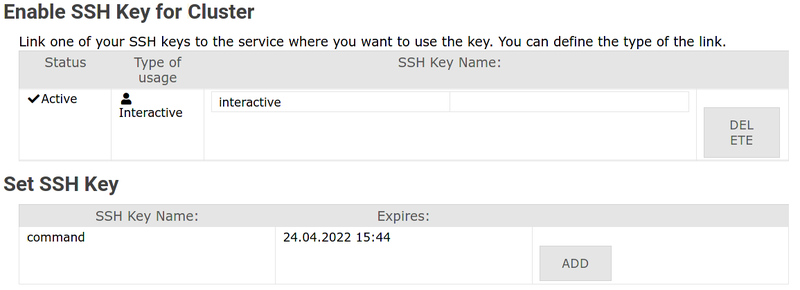
2. Navigate to "Registered Services" / "Registrierte Dienste"
Click Set SSH Key / SSH Key setzen for your cluster
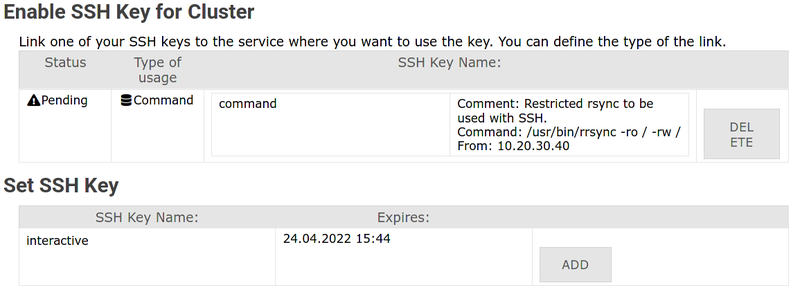
3. Find your key and click "Add" / "Hinzufügen"
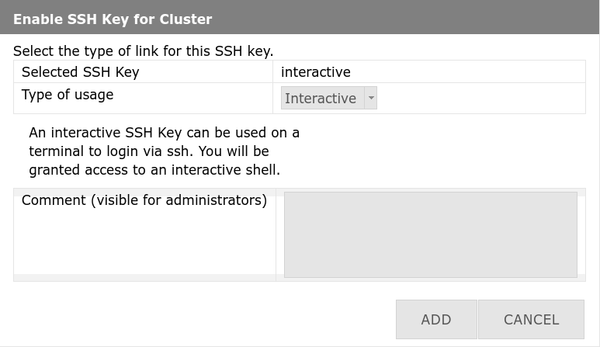
4. Select "Interactive" and confirm
- Usage type: Interactive
- Comment: Optional description
- Click Add / Hinzufügen
5. Done! Your key is active for interactive logins
Step 2B: Register Command Key
Command Keys enable automated workflows (e.g., backups, data transfers) without manual login.
Security Requirements
Command keys are always valid (no 2FA required), making them security-sensitive.
Mandatory restrictions:
- Single command: Specify exact command with full path
- IP restriction: Limit to specific IP address(es) or subnet
- Admin approval: Keys require review before activation
- Short validity: Maximum 30 days
Common use case: rrsync for data transfers
Registration Steps
1. Add your public key following Step 1 above
2. Navigate to "Registered Services"
Click Set SSH Key for your cluster
3. Find your key and click "Add" / "Hinzufügen"
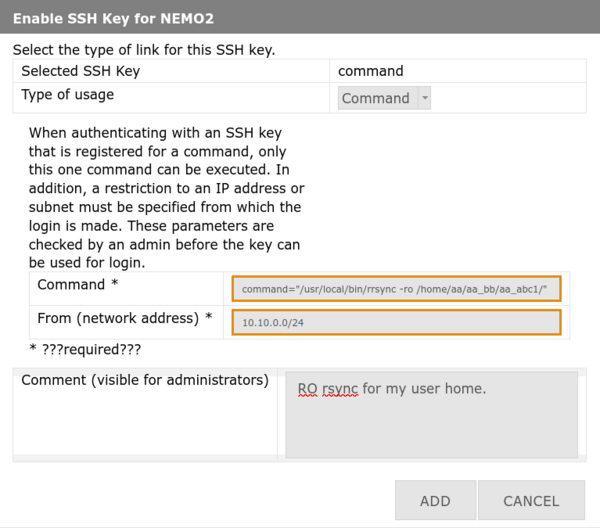
4. Configure command restrictions:
- Usage type: Select Command
- Command: Full path with parameters (see example below)
- From: IP address or CIDR notation (e.g.,
192.168.1.0/24) - Comment: Explain purpose (speeds up approval)
- Click Add / Hinzufügen
| Example: rrsync for data transfer |
|---|
/usr/local/bin/rrsync -ro /home/aa/aa_bb/aa_abc1/ Note: Verify exact path on your cluster (may be |
5. Wait for approval
Revoking SSH Keys
Note: Revoked keys are immediately disabled and cannot be reused.
1. Navigate to SSH key management:
- bwUniCluster 3.0 / NEMO 2 (bwIDM)
- bwForCluster Helix (bwServices)
2. Click "REVOKE" / "ZURÜCKZIEHEN" next to the key you want to disable
2. Click REVOKE / ZURÜCKZIEHEN next to the key you want to disable