Development/FFTW: Difference between revisions
S Richling (talk | contribs) m (S Richling moved page FFTW to Development/FFTW: Umzug in Development-Bereich) |
|||
| (66 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Softwarepage|numlib/mkl}} |
|||
{| width=600px class="wikitable" |
{| width=600px class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
| module load |
| module load |
||
| numlib/mkl |
| numlib/mkl |
||
|- |
|||
| Availability |
|||
| [[bwUniCluster_2.0]] | [[BwForCluster_JUSTUS_2]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| License |
| License |
||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
| No |
| No |
||
|} |
|} |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
= Description = |
= Description = |
||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
The '''Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL)''' offers FFTW2 (for version 2.x) and FFTW3 (for version 3.x) interfaces to the Intel MKL Fast Fourier Transform and Trigonometric Transform functionality. These interfaces enable applications using FFTW to gain performance with Intel MKL without changing the application source code. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use Intel MKL instead of a separate FFTW installation. |
The '''Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL)''' offers FFTW2 (for version 2.x) and FFTW3 (for version 3.x) interfaces to the Intel MKL Fast Fourier Transform and Trigonometric Transform functionality. These interfaces enable applications using FFTW to gain performance with Intel MKL without changing the application source code. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use Intel MKL instead of a separate FFTW installation. |
||
= |
= FAQ = |
||
Intel MKL is available on selected bwHPC-Clusters. A complete list of versions currently installed on the bwHPC-Clusters can be obtained from the [https://www.bwhpc.de/software.html Cluster Information System (CIS)]. |
|||
In order to check which versions of Intel MKL are installed on the compute cluster, run the following command: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ module avail numlib/mkl |
|||
</pre> |
|||
= Documentation = |
|||
A documentation for Intel MKL is available [https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/articles/intel-math-kernel-library-documentation.html online]. |
|||
The help page of the Intel MKL module provides more version specific information: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ module help numlib/mkl |
|||
----------- Module Specific Help for 'numlib/mkl/11.1.4' ---------- |
|||
This module provides the Intel(R) Math Kernel Library (MKL) |
|||
version 11.1.4, a fast and reliable implementation |
|||
of BLAS/LAPACK/FFTW (see also 'http://software.intel.com/en-us/intel-mkl/'). |
|||
The preferable compiler for this MKL version is 'compiler/intel/14.0'. Linking |
|||
with other compilers like GNU, PGI and SUN is possible. The desired compiler |
|||
module (exception system GNU compiler) has to be loaded before using MKL. |
|||
Local documentation: |
|||
Man pages in '$MKL_MAN_DIR/man3', e.g. 'man dotc'. |
|||
firefox $MKL_DOC_DIR/mkl_documentation.htm |
|||
acroread $MKL_DOC_DIR/l_mkl_11.1.4.211.mklman.pdf |
|||
acroread $MKL_DOC_DIR/l_mkl_11.1.4.211.mkl_11.1.4_lnx_userguide.pdf |
|||
[...] |
|||
[...] |
|||
</pre> |
|||
After loading the module, the environment variable <span style="background:#edeae2;margin:2px;padding:1px;border:1px dotted #808080">$MKL_DOC_DIR</span> points to the local documentation folder. |
|||
= Usage = |
|||
== Loading the module == |
|||
You can load the default version of Intel MKL with the following command: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ module load numlib/mkl |
|||
</pre> |
|||
The module will try to load all modules it needs to function (e.g., compiler, mpi, ...). If loading the module fails, check if you have already loaded one of those modules, but not in the version required by MKL. |
|||
If you wish to load another (older) version of Intel MKL, you can do so using |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ module load numlib/mkl/<version> |
|||
</pre> |
|||
with <version> specifying the desired version. |
|||
= Hints for compiling and linking = |
|||
== FFTW Specific Environments == |
|||
To see a list of all FFTW environments set by the 'module load'-command use the command |
|||
'module display numlib/fftw'. |
|||
<br> |
|||
After having loaded the appropriate module(s), you can use several environment variables to compile and link your application. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ module display numlib/fftw |
|||
------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|||
/opt/bwhpc/common/modulefiles/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1: |
|||
FTW_VERSION = 3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1 |
|||
FFTW_HOME = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1 |
|||
FFTW_BIN_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/bin |
|||
FFTW_INC_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/include |
|||
FFTW_LIB_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/lib |
|||
FFTW_STA_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/lib |
|||
FFTW_SHA_DIR = (empty) |
|||
FFTW_MAN_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/share/man |
|||
FFTW_INF_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/share/info |
|||
FFTW_DOC_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/doc |
|||
FFTW_EXA_DIR = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/examples |
|||
FFTW_WWW = http://www.fftw.org/ |
|||
PATH = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/bin:$PATH |
|||
MANPATH = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/share/man:$MANPATH |
|||
INFOPATH = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/share/info:$INFOPATH |
|||
LD_LIBRARY_PATH = /opt/bwhpc/common/numlib/fftw/3.3.3-impi-4.1.1-intel-13.1/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH |
|||
[...] |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Compile a Serial Program == |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ gcc example.c -o example -I$FFTW_INC_DIR -L$FFTW_LIB_DIR -lfftw3 -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
=== with POSIX Threads === |
|||
Compile program with support for POSIX threads. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ gcc example.c -o example -I$FFTW_INC_DIR -L$FFTW_LIB_DIR -lfftw3_threads -lfftw3 -lpthread -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Compile program with support for OpenMP threads == |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ gcc example.c -o example -fopenmp -I$FFTW_INC_DIR -L$FFTW_LIB_DIR -lfftw3_omp -lfftw3 -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Compile program with support for MPI == |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ mpicc example.c -o example -I$FFTW_INC_DIR -L$FFTW_LIB_DIR -lfftw3_mpi -lfftw3 -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
=== Run program with MPI support === |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ mpirun -n <ncpu> ./example |
|||
</pre> |
|||
(Replace <ncpu> by number of processor cores.) |
|||
Replace -lfftw3, -lfftw3_threads, etc. by -lfftw3f, -lfftw3f_threads, etc. for single |
|||
precision and by -lfftw3l, -lfftw3l_threads etc. for long-double precision codes, respectively. |
|||
[[File:comparison.png|right|border|300px|Copyright: KIZ (Ulm University)]] |
|||
These commands will compile your program with dynamic fftw library versions in |
|||
which case you also have to have the fftw module loaded for running the program. |
|||
Alternatively, you may want to link your program with static fftw library versions. |
|||
With static fftw libraries it is only necessary to load the fftw module for compiling |
|||
but not for executing the program. |
|||
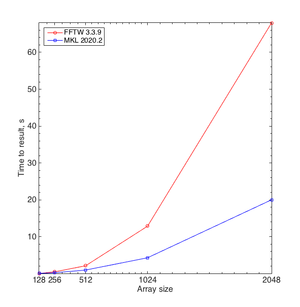
'''Q:''' Why is there no FFTW module on the cluster? |
|||
== Compile program with static fftw library versions == |
|||
Example for POSIX threads support |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ gcc example.c -o example -I$FFTW_INC_DIR $FFTW_LIB_DIR/{libfftw3_threads.a,libfftw3.a} -lpthread -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
or: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ gcc example.c -o example -I$FFTW_INC_DIR -L$FFTW_LIB_DIR -Wl,-Bstatic -lfftw3 -lfftw3_threads \ |
|||
-Wl,-Bdynamic -lpthread -lm |
|||
</pre> |
|||
[[#FFTW Specific Environments|Environment variables $FFTW_INC_DIR, $FFTW_LIB_DIR]] etc. are available after loading the module. |
|||
<br> |
|||
= Examples = |
|||
'''A:''' MKL exhibits better performance than FFTS libraries (see Figure on the right). Therefore, we recommend to use MKL and do not offer a separate FFTW installation. |
|||
Sometimes, FFTW is not available on your cluster. You can use the [[Math_Kernel_Library_(MKL)|MKL library]] instead and include the FFTW functions, too. Various examples can be found in $MKLROOT/examples. |
|||
'''Q:''' Why does my code complain about <span style="background:#edeae2;margin:2px;padding:1px;border:1px dotted #808080"> argument of type "long double *" is incompatible with parameter of type "double *" </span>? |
|||
If any assistance, please feel free to contact 'compchem [at] bwhpc.de' or submit a trouble ticket at https://www.bwhpc.de/supportportal. |
|||
'''A:''' The interfaces do not support long double precision because Intel MKL FFT functions operate only on single- and double-precision floating point data types. For the very rare case that you need extended data types, please submit a support ticket at https://www.bwhpc.de/supportportal. |
|||
<br> |
|||
Intel Math Kernel Library (MKL) offers FFTW2 and FFTW3 interfaces to Intel MKL Fast Fourier Transform and Trigonometric Transform functionality. The purpose of these interfaces is to enable applications using FFTW to gain performance with Intel MKL without changing the program source code. |
|||
<br> |
|||
Here is an excerpt from 'module help numlib/mkl': |
|||
<pre> |
|||
Static FFTW2/3 C/Fortran interfaces can be found in dir |
|||
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/ |
|||
Examples: |
|||
Link to FFTW3 Fortran interface with GNU compiler and ilp64 support: |
|||
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/fftw3xf/libfftw3xf_intel64_double_i8_gnu47.a |
|||
Link to FFTW3 Fortran interface with Intel compiler and lp64 support: |
|||
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/fftw3xf/libfftw3xf_intel64_double_i4_intel150.a |
|||
The Intel FFTW interfaces requires the Intel MKL library (e.g. it does |
|||
not work with ACML library). Usually it is not a problem to use a |
|||
different compiler version, e.g. to use _gnu41.a with gnu 4.3 compiler. |
|||
See dir ${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/ for other interfaces (fftw2/3 Fortran/C). |
|||
Compiler option for include files: -I${MKL_INC_DIR}/fftw |
|||
</pre> |
|||
= Useful links = |
= Useful links = |
||
| Line 193: | Line 44: | ||
* [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Math_Kernel_Library Wikipedia article (german)] |
* [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Math_Kernel_Library Wikipedia article (german)] |
||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Math_Kernel_Library Wikipedia article (english)] |
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Math_Kernel_Library Wikipedia article (english)] |
||
---- |
|||
[[Category:Numerical_libraries]][[Category:BwUniCluster]][[Category:BwUniCluster_2.0]][[Category:BwForCluster_Chemistry]][[Category:BwForCluster_JUSTUS_2]][[Category:BwForCluster_BinAC]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 00:04, 15 March 2023
|
The main documentation is available via |
| Description | Content |
|---|---|
| module load | numlib/mkl |
| License | Commercial. See EULA. |
| Citing | n/a |
| Links | Intel MKL Homepage | FFTW Homepage |
| Graphical Interface | No |
Description
The Fastest Fourier Transform in the West (FFTW) is a software library for computing discrete Fourier transforms in one or more dimensions, of arbitrary input size, and of both real and complex data (as well as of even/odd data, i.e. the discrete cosine/sine transforms or DCT/DST). FFTW was developed by Matteo Frigo and Steven G. Johnson at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
The Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL) offers FFTW2 (for version 2.x) and FFTW3 (for version 3.x) interfaces to the Intel MKL Fast Fourier Transform and Trigonometric Transform functionality. These interfaces enable applications using FFTW to gain performance with Intel MKL without changing the application source code. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use Intel MKL instead of a separate FFTW installation.
FAQ
Q: Why is there no FFTW module on the cluster?
A: MKL exhibits better performance than FFTS libraries (see Figure on the right). Therefore, we recommend to use MKL and do not offer a separate FFTW installation.
Q: Why does my code complain about argument of type "long double *" is incompatible with parameter of type "double *" ?
A: The interfaces do not support long double precision because Intel MKL FFT functions operate only on single- and double-precision floating point data types. For the very rare case that you need extended data types, please submit a support ticket at https://www.bwhpc.de/supportportal.