Sds-hd CIFS: Difference between revisions
m (→Prerequisites) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= <b> Prerequisites </b>= |
= <b> Prerequisites </b>= |
||
'''Attention:''' To access data served by SDS@hd via CIFS, You need a '''''Service Password'''''. See details [[Sds-hd_user_access]]. |
'''Attention:''' To access data served by SDS@hd via CIFS, You need a '''''Service Password'''''. See details [[Sds-hd_user_access|SDS@hd Access]]. |
||
Additionally the access to SDS@hd is currently only available inside the [https://www.belwue.de/netz/netz0.html belwue-Network]. |
Additionally the access to SDS@hd is currently only available inside the [https://www.belwue.de/netz/netz0.html belwue-Network]. |
||
This means you have to use the VPN Service of your HomeOrganization, if you want to access SDS@hd from outside the bwHPC-Clusters (e.g. via [https://www.eduroam.org/where/ eduroam] or from your personal Laptop) |
This means you have to use the VPN Service of your HomeOrganization, if you want to access SDS@hd from outside the bwHPC-Clusters (e.g. via [https://www.eduroam.org/where/ eduroam] or from your personal Laptop) |
||
= <b> Using SMB/CIFS for UNIX client </b> = |
|||
A UNIX like operating system needs a CIFS client to use a share. CIFS clients are part of Samba implementation for Linux and other UNIX like operating systems (http://www.samba.org) |
|||
'''Attention:''' |
|||
The core CIFS protocol does not provide unix ownership information or mode for files and directories. |
|||
Because of this, files and directories will generally appear to be owned by whatever values the uid= or gid= options are set, and will have permissions set to the default file_mode and dir_mode for the mount. '''Attempting to change these values via chmod/chown will return success but have no effect.''' |
|||
For security reasons, Server-side permission checks cannot be overriden. The permission checks done by the server will always correspond to the credentials used to mount the share, and not necessarily to the user who is accessing the share. |
|||
For this reason the mount option <pre>cifsacl</pre> together with a working '''ID Mapping''' setup is required, to allow correct permission handling and changes. It offers also the tools |
|||
<pre> |
|||
getcifsacl |
|||
setcifsacl |
|||
</pre> |
|||
to work with ACLs. |
|||
== ID Mapping == |
|||
Although mapping of POSIX UIDs and SIDs is not needed mounting a CIFS share '''it might become necessary when working with files on the share, e.g. when modifying ACLs'''. |
|||
With version 5.9 of cifs-utils a plugin interface was introduced by Jeff Layton to allow services other than winbind to handle the mapping of POSIX UIDs and SIDs. SSSD will provide a plugin to allow the cifs-utils to ask SSSD to map the ID. With this plugin a SSSD client can access a CIFS share with the same functionality as a client running Winbind. |
|||
For this reason we can use the same [[Sds-hd_nfs#configure kerberos environment for SDS@hd|SSSD setup]] for cifs like we use for the kerberized nfs-Setup. |
|||
Additionally we need the cifs packages: |
|||
* RedHat/CentOS: |
|||
<pre>> yum install cifs-utils</pre> |
|||
* debian/ubuntu: |
|||
<pre>> apt install cifs-utils</pre> |
|||
After installing SSSD you have to ensure that it will be used for cifs name resolution. e.g. |
|||
* RedHat/CentOS: |
|||
<pre>> alternatives --display cifs-idmap-plugin |
|||
cifs-idmap-plugin - Status ist automatisch. |
|||
Link verweist auf /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so |
|||
/usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so - priority 20 |
|||
/usr/lib64/cifs-utils/idmapwb.so - priority 10 |
|||
Zur Zeit ist die `best' Version /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so. |
|||
</pre> |
|||
* debian/ubuntu: |
|||
<pre>> update-alternatives --display idmap-plugin |
|||
idmap-plugin - automatischer Modus |
|||
beste Version des Links ist /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so |
|||
Link verweist zur Zeit auf /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so |
|||
Link idmap-plugin ist /etc/cifs-utils/idmap-plugin |
|||
Slave idmap-plugin.8.gz ist /usr/share/man/man8/idmap-plugin.8.gz |
|||
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/idmapwb.so - Priorität 20 |
|||
Slave idmap-plugin.8.gz: /usr/share/man/man8/idmapwb.8.gz |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== SMB Client == |
|||
'''Example:''' |
|||
To list the files in a SMB share, use the program smbclient. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
smbclient -U 'BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123' //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> |
|||
Enter BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123's password: |
|||
</pre> |
|||
The program allows you to access the files with a FTP like tool in an interactive shell. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
>smbclient //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> -U 'BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123' |
|||
Enter BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123's password: |
|||
smb: \> ls |
|||
. D 0 Thu Apr 23 12:51:48 2020 |
|||
.. D 0 Wed Apr 22 21:54:04 2020 |
|||
bench D 0 Fri Jul 26 10:24:05 2019 |
|||
benchmark_test D 0 Tue Oct 30 16:12:21 2018 |
|||
checksums D 0 Mon Sep 18 10:24:21 2017 |
|||
test.multiuser A 6 Thu Apr 23 12:36:07 2020 |
|||
test A 7 Thu Apr 23 09:38:13 2020 |
|||
..... |
|||
.snapshots DHR 0 Thu Jan 1 01:00:00 1970 |
|||
115343360000 blocks of size 1024. 108260302848 blocks available |
|||
smb:\ |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Mount a Share == |
|||
=== Single-User Environment === |
|||
A share can be mounted to a local directory, (e.g. /mnt/sds-hd ). Depending on your system setup, root privileges may be required. |
|||
==== Mount over command line ==== |
|||
'''Example:''' |
|||
<pre> |
|||
>mkdir /mnt/sds-hd |
|||
>mount -t cifs -o username=hd_xy123,domain=BWSERVICESAD,cifsacl //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> /mnt/sds-hd |
|||
Password: |
|||
or |
|||
> kinit hd_xy123 |
|||
Passwort für hd_xy123@BWSERVICES.UNI-HEIDELBERG.DE: |
|||
>mount -t cifs -o sec=krb5,cifsacl //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> /mnt/sds-hd |
|||
>df -h | grep sds-hd |
|||
//lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 108T 6,6T 101T 7% /mnt/sds-hd |
|||
>cd /mnt/sds-hd/ |
|||
>ls |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Verify the success of the mount invoking the mount command without any arguments: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
mount | grep sds-hd |
|||
//lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 on /mnt/sds-hd type cifs (rw,relatime,vers=3.0,cache=strict,username=xxxx,domain=BWSERVICESAD,uid=1000,forceuid,gid=0,noforcegid,addr=xxxxx,file_mode=0755,dir_mode=0755,soft,nounix,serverino,mapposix,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,echo_interval=60,actimeo=1) |
|||
</pre> |
|||
==== Mount over /etc/fstab ==== |
|||
Mounting a SDS@hd cifs share via /etc/fstab can be done by using username/password credentials or by using kerberos tickets. |
|||
'''Example:''' |
|||
<pre> |
|||
>mkdir /mnt/mountpoint |
|||
/etc/fstab |
|||
//lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv_acronym> /mnt/mountpoint cifs cifsacl,credentials=<path_to_user_HOME>/credentialsfile,noauto 0 0 |
|||
>cat /path_to_user_HOME/credentialsfile |
|||
username=hd_ xy123 |
|||
password=<your_servicepassword> |
|||
domain=BWSERVICESAD |
|||
or |
|||
/etc/fstab |
|||
//lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv_acronym> /mnt/mountpoint cifs cifsacl,sec=krb5,noauto 0 0 |
|||
> kinit hd_xy123 |
|||
Passwort für hd_xy123@BWSERVICES.UNI-HEIDELBERG.DE: |
|||
>mount /mnt/mountpoint |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Verify the success of the mount invoking the mount command without any arguments: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
mount | grep cifs |
|||
//lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 on /mnt/mountpoint type cifs (rw,relatime,vers=3.0,cache=strict,username=xxxx,domain=BWSERVICESAD,uid=1000,forceuid,gid=0,noforcegid,addr=xxxxx,file_mode=0755,dir_mode=0755,soft,nounix,serverino,mapposix,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,echo_interval=60,actimeo=1) |
|||
</pre> |
|||
=== Multiuser Environment === |
|||
By default, CIFS mounts only use a single set of user credentials (the mount credentials) when accessing a share. To support different user session on the same mountpoint the mount option <pre>multiuser</pre> has to be used. Because the kernel cannot prompt for passwords, '''multiuser mounts are limited to mounts using passwordless sec= options, like with [[Sds-hd_nfs|kerberos (sec=krb5)]]''' |
|||
==== AutoFS Setup ==== |
|||
Because cifs shares, in contrast to nfs-Mounts, has to be mounted directly, the root user can not simply mount them into a global folder. Instead the shares have to be initially mounted by a user who has access to the Speichervorhaben. To achieve this, we recommend the automounter "autofs". |
|||
* RedHat/CentOS: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
> yum install autofs |
|||
> systemctl enable autofs |
|||
> systemctl start autofs |
|||
</pre> |
|||
* debian/ubuntu: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
> apt install .... |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Afterwards you can configure the needed SDS@hd shares in a new map file: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
> cat /etc/auto.sds-hd |
|||
<sv-acronym1> -fstype=cifs,cifsacl,multiuser,sec=krb5,cruid=${UID},vers=3.0 ://lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym1> |
|||
<sv-acronym2> -fstype=cifs,cifsacl,multiuser,sec=krb5,cruid=${UID},vers=3.0 ://lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym2> |
|||
.... |
|||
</pre> |
|||
You have to include the new map into the auto.master file: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
cat /etc/auto.master |
|||
[...] |
|||
/mnt/sds-hd /etc/auto.sds-hd |
|||
[...] |
|||
</pre> |
|||
To display all available SDS@hd shares on this machine to the users, you should enable "browser_mode": |
|||
<pre> |
|||
cat /etc/autofs.conf |
|||
[...] |
|||
# to display all available SDS-hd shares on this to the users |
|||
browse_mode=yes |
|||
[...] |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Of course you can adopt all other autofs options, like timeouts, etc to the specific needs of your environment. |
|||
After changing the configuration, you should restart the autofs daemon |
|||
<pre> |
|||
systemctl restart autofs |
|||
</pre> |
|||
==== Access the Share ==== |
|||
Now each user should be able to mount a SDS@hd share, which is configured for this machine. If a share is allready mounted, other users will access this share with their own credentials without mounting again. |
|||
To get access, each user needs a valid kerberos ticket, which can be fetched with |
|||
<pre> |
|||
> kinit hd_xy123 |
|||
</pre> |
|||
= <b> Using SMB/CIFS for Windows client </b> = |
= <b> Using SMB/CIFS for Windows client </b> = |
||
Revision as of 15:30, 23 April 2020
Prerequisites
Attention: To access data served by SDS@hd via CIFS, You need a Service Password. See details SDS@hd Access.
Additionally the access to SDS@hd is currently only available inside the belwue-Network.
This means you have to use the VPN Service of your HomeOrganization, if you want to access SDS@hd from outside the bwHPC-Clusters (e.g. via eduroam or from your personal Laptop)
Using SMB/CIFS for UNIX client
A UNIX like operating system needs a CIFS client to use a share. CIFS clients are part of Samba implementation for Linux and other UNIX like operating systems (http://www.samba.org)
Attention: The core CIFS protocol does not provide unix ownership information or mode for files and directories. Because of this, files and directories will generally appear to be owned by whatever values the uid= or gid= options are set, and will have permissions set to the default file_mode and dir_mode for the mount. Attempting to change these values via chmod/chown will return success but have no effect.
For security reasons, Server-side permission checks cannot be overriden. The permission checks done by the server will always correspond to the credentials used to mount the share, and not necessarily to the user who is accessing the share.
For this reason the mount option
cifsacl
together with a working ID Mapping setup is required, to allow correct permission handling and changes. It offers also the tools
getcifsacl setcifsacl
to work with ACLs.
ID Mapping
Although mapping of POSIX UIDs and SIDs is not needed mounting a CIFS share it might become necessary when working with files on the share, e.g. when modifying ACLs.
With version 5.9 of cifs-utils a plugin interface was introduced by Jeff Layton to allow services other than winbind to handle the mapping of POSIX UIDs and SIDs. SSSD will provide a plugin to allow the cifs-utils to ask SSSD to map the ID. With this plugin a SSSD client can access a CIFS share with the same functionality as a client running Winbind.
For this reason we can use the same SSSD setup for cifs like we use for the kerberized nfs-Setup.
Additionally we need the cifs packages:
- RedHat/CentOS:
> yum install cifs-utils
- debian/ubuntu:
> apt install cifs-utils
After installing SSSD you have to ensure that it will be used for cifs name resolution. e.g.
- RedHat/CentOS:
> alternatives --display cifs-idmap-plugin cifs-idmap-plugin - Status ist automatisch. Link verweist auf /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so - priority 20 /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/idmapwb.so - priority 10 Zur Zeit ist die `best' Version /usr/lib64/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so.
- debian/ubuntu:
> update-alternatives --display idmap-plugin idmap-plugin - automatischer Modus beste Version des Links ist /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so Link verweist zur Zeit auf /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/cifs_idmap_sss.so Link idmap-plugin ist /etc/cifs-utils/idmap-plugin Slave idmap-plugin.8.gz ist /usr/share/man/man8/idmap-plugin.8.gz /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cifs-utils/idmapwb.so - Priorität 20 Slave idmap-plugin.8.gz: /usr/share/man/man8/idmapwb.8.gz
SMB Client
Example: To list the files in a SMB share, use the program smbclient.
smbclient -U 'BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123' //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> Enter BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123's password:
The program allows you to access the files with a FTP like tool in an interactive shell.
>smbclient //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> -U 'BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123'
Enter BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123's password:
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Thu Apr 23 12:51:48 2020
.. D 0 Wed Apr 22 21:54:04 2020
bench D 0 Fri Jul 26 10:24:05 2019
benchmark_test D 0 Tue Oct 30 16:12:21 2018
checksums D 0 Mon Sep 18 10:24:21 2017
test.multiuser A 6 Thu Apr 23 12:36:07 2020
test A 7 Thu Apr 23 09:38:13 2020
.....
.snapshots DHR 0 Thu Jan 1 01:00:00 1970
115343360000 blocks of size 1024. 108260302848 blocks available
smb:\
Single-User Environment
A share can be mounted to a local directory, (e.g. /mnt/sds-hd ). Depending on your system setup, root privileges may be required.
Mount over command line
Example:
>mkdir /mnt/sds-hd >mount -t cifs -o username=hd_xy123,domain=BWSERVICESAD,cifsacl //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> /mnt/sds-hd Password: or > kinit hd_xy123 Passwort für hd_xy123@BWSERVICES.UNI-HEIDELBERG.DE: >mount -t cifs -o sec=krb5,cifsacl //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym> /mnt/sds-hd >df -h | grep sds-hd //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 108T 6,6T 101T 7% /mnt/sds-hd >cd /mnt/sds-hd/ >ls
Verify the success of the mount invoking the mount command without any arguments:
mount | grep sds-hd //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 on /mnt/sds-hd type cifs (rw,relatime,vers=3.0,cache=strict,username=xxxx,domain=BWSERVICESAD,uid=1000,forceuid,gid=0,noforcegid,addr=xxxxx,file_mode=0755,dir_mode=0755,soft,nounix,serverino,mapposix,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,echo_interval=60,actimeo=1)
Mount over /etc/fstab
Mounting a SDS@hd cifs share via /etc/fstab can be done by using username/password credentials or by using kerberos tickets.
Example:
>mkdir /mnt/mountpoint /etc/fstab //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv_acronym> /mnt/mountpoint cifs cifsacl,credentials=<path_to_user_HOME>/credentialsfile,noauto 0 0 >cat /path_to_user_HOME/credentialsfile username=hd_ xy123 password=<your_servicepassword> domain=BWSERVICESAD or /etc/fstab //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv_acronym> /mnt/mountpoint cifs cifsacl,sec=krb5,noauto 0 0 > kinit hd_xy123 Passwort für hd_xy123@BWSERVICES.UNI-HEIDELBERG.DE: >mount /mnt/mountpoint
Verify the success of the mount invoking the mount command without any arguments:
mount | grep cifs //lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/sd16j007 on /mnt/mountpoint type cifs (rw,relatime,vers=3.0,cache=strict,username=xxxx,domain=BWSERVICESAD,uid=1000,forceuid,gid=0,noforcegid,addr=xxxxx,file_mode=0755,dir_mode=0755,soft,nounix,serverino,mapposix,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,echo_interval=60,actimeo=1)
Multiuser Environment
By default, CIFS mounts only use a single set of user credentials (the mount credentials) when accessing a share. To support different user session on the same mountpoint the mount option
multiuser
has to be used. Because the kernel cannot prompt for passwords, multiuser mounts are limited to mounts using passwordless sec= options, like with kerberos (sec=krb5)
AutoFS Setup
Because cifs shares, in contrast to nfs-Mounts, has to be mounted directly, the root user can not simply mount them into a global folder. Instead the shares have to be initially mounted by a user who has access to the Speichervorhaben. To achieve this, we recommend the automounter "autofs".
- RedHat/CentOS:
> yum install autofs > systemctl enable autofs > systemctl start autofs
- debian/ubuntu:
> apt install ....
Afterwards you can configure the needed SDS@hd shares in a new map file:
> cat /etc/auto.sds-hd
<sv-acronym1> -fstype=cifs,cifsacl,multiuser,sec=krb5,cruid=${UID},vers=3.0 ://lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym1>
<sv-acronym2> -fstype=cifs,cifsacl,multiuser,sec=krb5,cruid=${UID},vers=3.0 ://lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym2>
....
You have to include the new map into the auto.master file:
cat /etc/auto.master [...] /mnt/sds-hd /etc/auto.sds-hd [...]
To display all available SDS@hd shares on this machine to the users, you should enable "browser_mode":
cat /etc/autofs.conf [...] # to display all available SDS-hd shares on this to the users browse_mode=yes [...]
Of course you can adopt all other autofs options, like timeouts, etc to the specific needs of your environment. After changing the configuration, you should restart the autofs daemon
systemctl restart autofs
Now each user should be able to mount a SDS@hd share, which is configured for this machine. If a share is allready mounted, other users will access this share with their own credentials without mounting again.
To get access, each user needs a valid kerberos ticket, which can be fetched with
> kinit hd_xy123
Using SMB/CIFS for Windows client
You can use a CIFS share from a Microsoft operating system.
Adopting Universal Naming Convention (UNC) syntax
Use Windows Explorer entering the path to the share in UNC syntax:
Examples:
\\lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de or \\lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de\<sv-acronym>
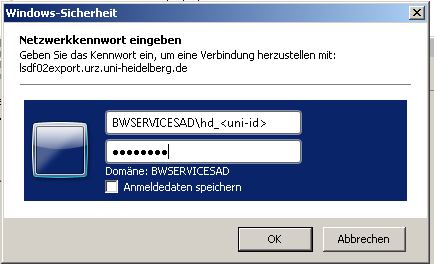
Following the input of the UNC path, a window will pop up:
Loginname: BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123
Password: Service Password
Following authentication a new window pops up, showing the content of the share.
You can now manipulate your files as accustomed.
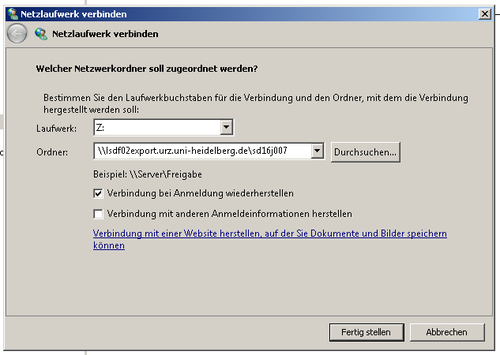
Creation of a network (pseudo) drive with Windows Explorer
To connect to a network share in Windows Explorer select the control field
Select a drive letter to be associated with the network share and enter the network path (e.g. \\lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de). Select ‘use a different identification‘, as these differ from your credential used locally.
Path: \\lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de\<sv-acronym>
Username: BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123
Password: Service Password
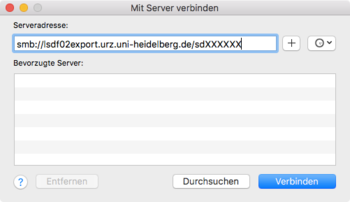
Using SMB/CIFS for Mac OS client
Creation of a network drive with Finder
To connect to a network share in Finder select the control field
Select a drive letter to be associated with the network share and enter the network path (e.g. \\lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de). Select ‘use a different identification‘, as these differ from your credential used locally.
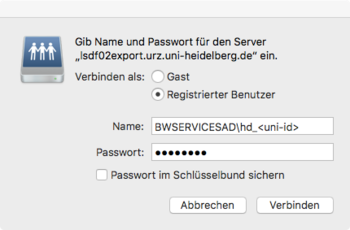
Path: smb://lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/<sv-acronym>
Username: BWSERVICESAD\hd_xy123
Password: Service Password