Development/FFTW
| Description | Content |
|---|---|
| module load | numlib/mkl |
| Availability | bwUniCluster_2.0 | BwForCluster_JUSTUS_2 |
| License | Commercial. See EULA. |
| Citing | n/a |
| Links | Intel MKL Homepage | FFTW Homepage |
| Graphical Interface | No |
Description
The Fastest Fourier Transform in the West (FFTW) is a software library for computing discrete Fourier transforms in one or more dimensions, of arbitrary input size, and of both real and complex data (as well as of even/odd data, i.e. the discrete cosine/sine transforms or DCT/DST). FFTW was developed by Matteo Frigo and Steven G. Johnson at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
The Intel Math Kernel Library (Intel MKL) offers FFTW2 (for version 2.x) and FFTW3 (for version 3.x) interfaces to the Intel MKL Fast Fourier Transform and Trigonometric Transform functionality. These interfaces enable applications using FFTW to gain performance with Intel MKL without changing the application source code. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use Intel MKL instead of a separate FFTW installation.
Availability
Intel MKL is available on selected bwHPC-Clusters. A complete list of versions currently installed on the bwHPC-Clusters can be obtained from the Cluster Information System (CIS).
In order to check which versions of Intel MKL are installed on the compute cluster, run the following command:
$ module avail numlib/mkl
Documentation
A documentation for Intel MKL is available online.
The help page of the Intel MKL module provides more version specific information:
$ module help numlib/mkl
----------- Module Specific Help for 'numlib/mkl/11.1.4' ----------
This module provides the Intel(R) Math Kernel Library (MKL)
version 11.1.4, a fast and reliable implementation
of BLAS/LAPACK/FFTW (see also 'http://software.intel.com/en-us/intel-mkl/').
The preferable compiler for this MKL version is 'compiler/intel/14.0'. Linking
with other compilers like GNU, PGI and SUN is possible. The desired compiler
module (exception system GNU compiler) has to be loaded before using MKL.
Local documentation:
Man pages in '$MKL_MAN_DIR/man3', e.g. 'man dotc'.
firefox $MKL_DOC_DIR/mkl_documentation.htm
acroread $MKL_DOC_DIR/l_mkl_11.1.4.211.mklman.pdf
acroread $MKL_DOC_DIR/l_mkl_11.1.4.211.mkl_11.1.4_lnx_userguide.pdf
[...]
Static FFTW2/3 C/Fortran interfaces can be found in dir
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/
Examples:
Link to FFTW3 Fortran interface with GNU compiler and ilp64 support:
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/fftw3xf/libfftw3xf_intel64_double_i8_gnu47.a
Link to FFTW3 Fortran interface with Intel compiler and lp64 support:
${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/fftw3xf/libfftw3xf_intel64_double_i4_intel150.a
The Intel FFTW interfaces requires the Intel MKL library (e.g. it does
not work with ACML library). Usually it is not a problem to use a
different compiler version, e.g. to use _gnu41.a with gnu 4.3 compiler.
See dir ${MKL_HOME}/interfaces/ for other interfaces (fftw2/3 Fortran/C).
Compiler option for include files: -I${MKL_INC_DIR}/fftw
[...]
After loading the module, the environment variable $MKL_DOC_DIR points to the local documentation folder.
Usage
Loading the module
You can load the default version of Intel MKL with the following command:
$ module load numlib/mkl
The module will try to load all modules it needs to function (e.g., compiler, mpi, ...). If loading the module fails, check if you have already loaded one of those modules, but not in the version required by MKL.
If you wish to load another (older) version of Intel MKL, you can do so using
$ module load numlib/mkl/<version>
with <version> specifying the desired version.
FFTW Interface to Intel MKL
To include the proper header files use the compiler option
-I${MKL_INC_DIR}/fftw
If you want to link dynamically against the FFTW functions you can just use the flag
-mkl
but when using static linking you have to link against the correct library in the directory $MKL_HOME/interfaces/.
If you need any assistance, please feel free to contact 'compchem [at] bwhpc.de' or submit a trouble ticket at https://www.bwhpc.de/supportportal.
Examples
Consider the following FFTW task:
/*
* fftw test -- double precision
*
* icc -std=c99 fftw3-test.c -o example -mkl -I${MKL_INC_DIR}/fftw
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fftw3.h>
#define N 8
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
double in1[] = { 0.00000, 0.12467, 0.24740, 0.36627,
0.47943, 0.58510, 0.68164, 0.76754
};
double in2[N];
fftw_complex out[N / 2 + 1];
fftw_plan p1, p2;
p1 = fftw_plan_dft_r2c_1d(N, in1, out, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
p2 = fftw_plan_dft_c2r_1d(N, out, in2, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
fftw_execute(p1);
fftw_execute(p2);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
printf("%2d %15.10f %15.10f\n", i, in1[i], in2[i] / N);
}
fftw_destroy_plan(p1);
fftw_destroy_plan(p2);
return 0;
}
It can be compiled and executed with the following commands:
$ module load compiler/intel/19.1.2
$ module load numlib/mkl/2020.2
$ icc -std=c99 fftw3-test.c -o example -mkl -I${MKL_INC_DIR}/fftw
$ ./example
Further examples can be found in $MKLROOT/examples.
FAQ
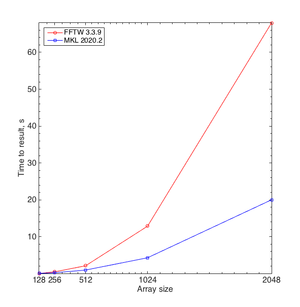
Q: Why does no separate FFTW module exist on the cluster?
A: MKL is more performant (see, Figure on the right). Therefore, we would like to advice you that you use MKL and decided not to offer a separate FFTW installation.
Q: Why does my code crash with an error message suggesting undefined reference to `fftwl_<...>' ?
A: The interfaces do not support long double precision because Intel MKL FFT functions operate only on single- and double-precision floating point data types. For the very rare case that you need extended data types, please contact 'compchem [at] bwhpc.de' or submit a trouble ticket at https://www.bwhpc.de/supportportal.