BinAC2/Software/AMDock: Difference between revisions
F Bartusch (talk | contribs) (Created page with "stub") |
F Bartusch (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| width=700px class="wikitable" |
|||
stub |
|||
|- |
|||
! Description !! Content |
|||
|- |
|||
| module load |
|||
| chem/amdock |
|||
|- |
|||
| License |
|||
| [https://github.com/Valdes-Tresanco-MS/AMDock?tab=GPL-3.0-1-ov-file GPL-3.0] |
|||
|- |
|||
| Links |
|||
| [https://github.com/Valdes-Tresanco-MS/AMDock GitHub] |
|||
|- |
|||
| Graphical Interface |
|||
| Yes |
|||
|} |
|||
= Description = |
|||
AMDock (Assisted Molecular Docking) is a user-friendly graphical tool to assist in the docking of protein-ligand complexes using Autodock-Vina or AutoDock4. This tool integrates several external programs for processing docking input files, define the search space (box) and perform docking under user’s supervision. |
|||
You can use the AMDock graphical user interface on BinAC 2 via TigerVNC. The AMDock provides an ready to use example jobscript. |
|||
= Usage = |
|||
== VNC viewer == |
|||
First, you will need an VNC viewer on your local workstation. Please refer to the [https://wiki.bwhpc.de/e/BinAC2/Software/TigerVNC#VNC_viewer TigerVNC documentation] for installing the VNC viewer. |
|||
== Start AMDock == |
|||
The AMDock module provides a ready to use example jobscript. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
# Load AMDock module |
|||
module load chem/amdock/1.6.2 |
|||
# Copy the jobscript into your current working directory |
|||
cp $AMDOCK_EXA_DIR/binac2-amdock-1.6.2-example.slurm . |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Adjust needed resources (cpus, memory, time) as needed. Please don't touch anything else. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
# Adjust these values as needed |
|||
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=10 |
|||
#SBATCH --mem=20gb |
|||
#SBATCH --time=6:00:00 |
|||
# Don't change these settings |
|||
#SBATCH --nodes=1 |
|||
#SBATCH --partition=interactive |
|||
#SBATCH --gres=display:1 |
|||
#SBATCH --signal=B:SIGUSR1@60 |
|||
#SBATCH --job-name=amdock-1.6.2 |
|||
module load chem/amdock/1.6.2 |
|||
# AMDock is used via a graphical user interface (GUI) |
|||
# We need to start a VNC server in order to work with |
|||
# AMDock |
|||
# This wrapper script will start the VNC server and prints |
|||
# connection details to the job's stdout file |
|||
amdock_wrapper |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Submit the AMDock job. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
jobid=$(sbatch --parsable binac2-amdock-1.6.2-example.slurm) |
|||
</pre> |
|||
== Create SSH tunnel == |
|||
The compute node on which AMDock is running is not directly reachable from your local workstation. Therefore, you need to create an SSH tunnel from your workstation to the compute node via the BinAC 2 login node. |
|||
The job's standard output file (<code>slurm-${jobid}.out</code>) contains all the information you need. Please note that details such as the IP address, port number, and access URL will differ in your case. |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ cat slurm-${jobid}.out |
|||
[...] |
|||
Paste this ssh command in a terminal on local host (i.e., laptop) |
|||
----------------------------------------------------------------- |
|||
ssh -N -L 5901:172.0.0.1:5901 tu_iioba01@login.binac2.uni-tuebingen.de |
|||
Then you can connect to the session with your local vncviewer: |
|||
----------------------------------------------------------------- |
|||
vncviewer localhost:5901 |
|||
[...] |
|||
</pre> |
|||
Linux users can simply copy&paste the <code>ssh -N -L ...</code> command into their terminal. |
|||
Windows users, please refer to [https://wiki.bwhpc.de/e/BinAC2/Software/Jupyterlab#Windows_Users this documentation]. It's about JupyterLab, but the SSH-tunnel is created in a similar way. |
|||
== Connect to VNC Server == |
|||
Now you can use your local VNC viewer and access the VNC session. Please use the correct port you got when starting the VNC server. At some point you will need to enter the password you create earlier. |
|||
=== Windows === |
|||
TODO |
|||
=== Linux === |
|||
<pre> |
|||
vncviewer localhost:5901 |
|||
</pre> |
|||
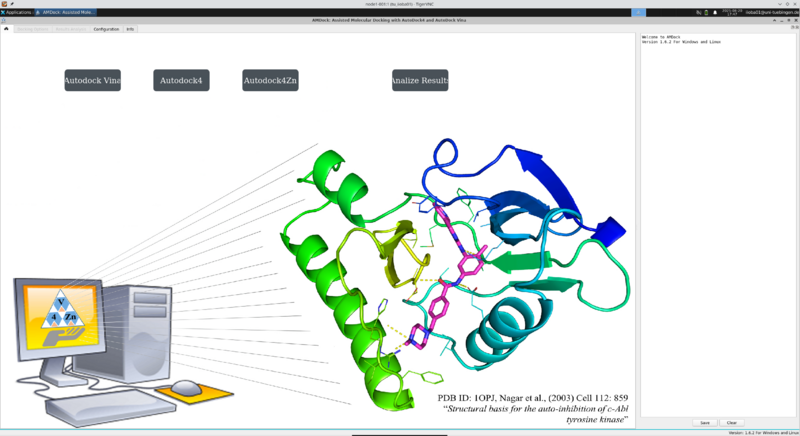
You should be greeted with the virtual desktop running AMDock. |
|||
[[File:Binac2-amdock.png | 800px | center | Xterm opened in VNC viewer]] |
|||
Attention: If you close the AMDock window the VNCserver, as well as the interactive job, will be stopped. |
|||
Revision as of 17:50, 20 August 2025
| Description | Content |
|---|---|
| module load | chem/amdock |
| License | GPL-3.0 |
| Links | GitHub |
| Graphical Interface | Yes |
Description
AMDock (Assisted Molecular Docking) is a user-friendly graphical tool to assist in the docking of protein-ligand complexes using Autodock-Vina or AutoDock4. This tool integrates several external programs for processing docking input files, define the search space (box) and perform docking under user’s supervision.
You can use the AMDock graphical user interface on BinAC 2 via TigerVNC. The AMDock provides an ready to use example jobscript.
Usage
VNC viewer
First, you will need an VNC viewer on your local workstation. Please refer to the TigerVNC documentation for installing the VNC viewer.
Start AMDock
The AMDock module provides a ready to use example jobscript.
# Load AMDock module module load chem/amdock/1.6.2 # Copy the jobscript into your current working directory cp $AMDOCK_EXA_DIR/binac2-amdock-1.6.2-example.slurm .
Adjust needed resources (cpus, memory, time) as needed. Please don't touch anything else.
#!/bin/bash # Adjust these values as needed #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=10 #SBATCH --mem=20gb #SBATCH --time=6:00:00 # Don't change these settings #SBATCH --nodes=1 #SBATCH --partition=interactive #SBATCH --gres=display:1 #SBATCH --signal=B:SIGUSR1@60 #SBATCH --job-name=amdock-1.6.2 module load chem/amdock/1.6.2 # AMDock is used via a graphical user interface (GUI) # We need to start a VNC server in order to work with # AMDock # This wrapper script will start the VNC server and prints # connection details to the job's stdout file amdock_wrapper
Submit the AMDock job.
jobid=$(sbatch --parsable binac2-amdock-1.6.2-example.slurm)
Create SSH tunnel
The compute node on which AMDock is running is not directly reachable from your local workstation. Therefore, you need to create an SSH tunnel from your workstation to the compute node via the BinAC 2 login node.
The job's standard output file (slurm-${jobid}.out) contains all the information you need. Please note that details such as the IP address, port number, and access URL will differ in your case.
$ cat slurm-${jobid}.out
[...]
Paste this ssh command in a terminal on local host (i.e., laptop)
-----------------------------------------------------------------
ssh -N -L 5901:172.0.0.1:5901 tu_iioba01@login.binac2.uni-tuebingen.de
Then you can connect to the session with your local vncviewer:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
vncviewer localhost:5901
[...]
Linux users can simply copy&paste the ssh -N -L ... command into their terminal.
Windows users, please refer to this documentation. It's about JupyterLab, but the SSH-tunnel is created in a similar way.
Connect to VNC Server
Now you can use your local VNC viewer and access the VNC session. Please use the correct port you got when starting the VNC server. At some point you will need to enter the password you create earlier.
Windows
TODO
Linux
vncviewer localhost:5901
You should be greeted with the virtual desktop running AMDock.
Attention: If you close the AMDock window the VNCserver, as well as the interactive job, will be stopped.