NEMO2/Slurm and SDS@hd/Access: Difference between pages
H Schumacher (talk | contribs) m (Update Access via BinAC) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page provides an overview on how to access data served by SDS@hd. To get an introduction to data transfer in general, see [[Data_Transfer|data transfer]]. |
|||
The bwForCluster NEMO 2 uses Slurm ([https://slurm.schedmd.com/ https://slurm.schedmd.com/]) for scheduling compute jobs. |
|||
== Prerequisites == |
|||
= Slurm Command Overview = |
|||
* You need to be [[SDS@hd/Registration|registered]]. |
|||
{| width=750px class="wikitable" |
|||
* You need to be in the belwue-Network. This means you have to use the VPN Service of your HomeOrganization, if you want to access SDS@hd from outside the bwHPC-Clusters (e.g. via eduroam or from your personal notebook). |
|||
! Slurm commands !! Brief explanation |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/sbatch.html sbatch] || Submits a job and queues it in an input queue |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/salloc.html salloc] || Request resources for an interactive job |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/squeue.html squeue] || Displays information about active, eligible, blocked, and/or recently completed jobs |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/scontrol.html scontrol] || Displays detailed job state information |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/sstat.html sstat] || Displays status information about a running job |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://slurm.schedmd.com/scancel.html scancel] || Cancels a job |
|||
|- |
|||
| seff || Shows the "job efficiency" of a job after it has finished |
|||
|} |
|||
== Needed Information, independent of the chosen tool == |
|||
= Submitting Jobs on the bwForCluster NEMO 2 = |
|||
* [[Registration/Login/Username| Username]]: Same as for the bwHPC Clusters |
|||
Batch jobs are submitted with the command: |
|||
* Password: The Service Password that you set at bwServices in the [[SDS@hd/Registration|registration step]]. |
|||
* SV-Acronym: Use the lower case version of the acronym for all access options. |
|||
* Hostname: The hostname depends on the chosen network protocol: |
|||
** For [[Data_Transfer/SSHFS|SSHFS]] and [[Data_Transfer/SFTP|SFTP]]: ''lsdf02-sshfs.urz.uni-heidelberg.de'' |
|||
** For [[SDS@hd/Access/SMB|SMB]] and [[SDS@hd/Access/NFS|NFS]]: ''lsdf02.urz.uni-heidelberg.de'' |
|||
** For [[Data_Transfer/WebDAV|WebDAV]] the url is: ''https://lsdf02-webdav.urz.uni-heidelberg.de'' |
|||
== Recommended Setup == |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash>$ sbatch <job-script></syntaxhighlight> |
|||
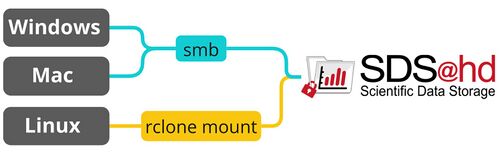
The following graphic shows the recommended way for accessing SDS@hd via Windows/Mac/Linux. The table provides an overview of the most important access options and links to the related pages.<br /> |
|||
If you have various use cases, it is recommended to use [[Data_Transfer/Rclone|Rclone]]. You can copy, sync and mount with it. Thanks to its multithreading capability Rclone is a good fit for transferring big data.<br /> |
|||
For an overview of all connection possibilities, please have a look at [[Data_Transfer/All_Data_Transfer_Routes|all data transfer routes]]. |
|||
[[File:Data_transfer_diagram_simple.jpg|center|500px]] |
|||
A job script contains options for Slurm in lines beginning with <code>#SBATCH</code> as well as your commands which you want to execute on the compute nodes. For example: |
|||
<p style="text-align: center; font-size: small; margin-top: 10px">Figure 1: SDS@hd main transfer routes</p> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang='bash'> |
|||
|- style="font-weight:bold; text-align:center; vertical-align:middle;" |
|||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
! |
|||
#SBATCH --nodes=1 |
|||
! Use Case |
|||
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 |
|||
! Windows |
|||
#SBATCH --time=00:14:00 |
|||
! Mac |
|||
#SBATCH --mem=1gb |
|||
! Linux |
|||
echo 'Here starts the calculation' |
|||
! Possible Bandwith |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
! Firewall Ports |
|||
You can override options from the script on the command-line: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang=bash>$ sbatch --time=03:00:00 <job-script></syntaxhighlight> |
|||
== Resource Requests == |
|||
Important resource request options for the Slurm command sbatch are: |
|||
{| width=750px class="wikitable" |
|||
! Option !! Slurm (sbatch) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Data_Transfer/Rclone|Rclone]] + <protocol> |
|||
| #SBATCH|| Script directive |
|||
| copy, sync and mount, multithreading |
|||
| ✓ |
|||
| ✓ |
|||
| ✓ |
|||
| depends on used protocol |
|||
| depends on used protocol |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/SMB|SMB]] |
|||
| --time=<hh:mm:ss> (-t <hh:mm:ss>)|| Wall time limit |
|||
| mount as network drive in file explorer or usage via Rclone |
|||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/SMB#Windows|✓]] |
|||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/SMB#Mac|✓]] |
|||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/SMB#Linux|✓]] |
|||
| up to 40 Gbit/sec |
|||
| 139 (netbios), 135 (rpc), 445 (smb) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Data_Transfer/WebDAV|WebDAV]] |
|||
| --job-name=<name> (-J <name>)|| Job name |
|||
| go to solution for restricted networks |
|||
|- |
|||
| [✓] |
|||
| --nodes=<count> (-N <count>)|| Node count |
|||
| ✓ |
|||
|- |
|||
| ✓ |
|||
| --ntasks=<count> (-n <count>)|| Core count |
|||
| up to 100GBit/sec |
|||
|- |
|||
| 80 (http), 443 (https) |
|||
| --ntasks-per-node=<count>|| Process count per node |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:middle;" |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/Graphical_Clients#MobaXterm|MobaXterm]] |
|||
| --mem=<limit>|| Memory limit per node |
|||
| Graphical User Interface (GUI) |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/Graphical_Clients#MobaXterm|✓]] |
|||
| --mem-per-cpu=<limit>|| Memory limit per process |
|||
| ☓ |
|||
|- |
|||
| ☓ |
|||
| --gres=gpu:<count>|| GPU count (gres = "generic resource") |
|||
| see sftp |
|||
|- |
|||
| see sftp |
|||
| --gres=scratch:<count> || Disk space of <count> GB per requested task |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:middle;" |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/NFS|NFS]] |
|||
| --exclusive|| Node exclusive job |
|||
| mount for multi-user environments |
|||
| ☓ |
|||
| ☓ |
|||
| [[SDS@hd/Access/NFS|✓]] |
|||
| up to 40 Gbit/sec |
|||
| - |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:middle;" |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SSHFS|SSHFS]] |
|||
| mount, needs stable internet connection |
|||
| ☓ |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SSHFS#MacOS_&_Linux|✓]] |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SSHFS#MacOS_&_Linux|✓]] |
|||
| see sftp |
|||
| see sftp |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:middle;" |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SFTP|SFTP]] |
|||
| interactive shell, better usability when used together with Rclone |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SFTP#Windows|✓]] |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SFTP#MacOS_&_Linux|✓]] |
|||
| [[Data_Transfer/SFTP#MacOS_&_Linux|✓]] |
|||
| up to 40 Gbit/sec |
|||
| 22 (ssh) |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
<p style="text-align: center; font-size: small; margin-top: 10px">Table 1: SDS@hd transfer routes</p> |
|||
=== Access from a bwHPC Cluster === |
|||
'''Nodes and Cores''' |
|||
Slurm provides a number of options to request nodes and cores. |
|||
Typically, using <code>--nodes=<count></code> and <code>--ntasks-per-node=<count></code> should work for all your jobs. For single core jobs, it would be sufficient to use the option <code>--ntasks=1</code>. Specifying only <code>--ntasks</code> may lead to slurm trying to distribute tasks over more than one node even if you requested a small amount of cores. |
|||
'''Memory''' |
|||
Memory can be requested with either the option <code>--mem=<limit></code> (memory per node) or <code>--mem-per-cpu=<limit></code> (memory per process). When looking up the maximum available memory for a certain node type subtract about 5 GB for the operating system. Specify the memory limit as a value-unit-pair, for example 500mb or 8gb. |
|||
In most cases it is preferable to use the <code>--mem=<limit></code> option. |
|||
'''GPUs''' |
|||
GPUs are requested as "generic resources" with <code>--gres:gpu:<count></code>. |
|||
== Default Values == |
|||
Default values for jobs are: |
|||
* Runtime: --time=01:00:00 (1 hour) |
|||
* Nodes: --nodes=1 (one node) |
|||
* Tasks: --tasks-per-node=1 (one task per node) |
|||
* Cores: --cpus-per-task=1 (one core per task) |
|||
* Memory: --mem-per-cpu=1gb (1 GB per core) |
|||
== Partitions == |
|||
On bwForCluster NEMO 2 it is '''optional''' to request a partition with '--partition=<partition_name>' on job submission. Within a partition job allocations are routed automatically to the most suitable compute node(s) for the requested resources (e.g. amount of nodes and cores, memory, number of GPUs). The "CPU" partition is the default partition, if no partition is requested. |
|||
The partitions cpu, milan and genoa are operated in shared mode, i.e. jobs from different users can run on the same node. Jobs can get exclusive access to compute nodes in these partitions with the "--exclusive" option. |
|||
GPUs will follow within the next weeks. |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="width:20%"| Partition |
|||
! style="width:20%"| Node Access Policy |
|||
! style="width:20%"| Nodes |
|||
! style="width:20%"| Default |
|||
! style="width:20%"| Limits |
|||
|- |
|||
| cpu |
|||
| shared |
|||
| milan, genoa |
|||
| ntasks=1, time=01:00:00, mem-per-cpu=1gb |
|||
| time=96:00:00 |
|||
|- |
|||
| genoa |
|||
| shared |
|||
| genoa |
|||
| ntasks=1, time=01:00:00, mem-per-cpu=1gb |
|||
| time=96:00:00 |
|||
|- |
|||
| milan (currently offline) |
|||
| shared |
|||
| milan |
|||
| ntasks=1, time=01:00:00, mem-per-cpu=1gb |
|||
| time=96:00:00 |
|||
|} |
|||
== Monitoring Jobs with squeue == |
|||
After you submitted the job, you can see it waiting using the <code>squeue</code> command: |
|||
(also read the man page with <code>man squeue</code> for more information on how to use the command) |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang='shell'> |
|||
> squeue |
|||
JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON) |
|||
426 cpu 20k fr_0123 R 0:02 2 n[4101-4102] |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
Output shows: |
|||
* JOBID: the jobid is an unique number your job gets |
|||
* PARTITION: the cluster can be divided in different types of nodes. |
|||
* NAME: the name you gave your job with the --job-name= option |
|||
* USER: your username |
|||
* ST: the state the job is in. R = running, PD = pending, CD = completed. See man page for a full list on states. |
|||
* TIME: how long the job has been running |
|||
* NODES: how many nodes were requested |
|||
* NODELIST(REASON): either show the node(s) the job is running on, or a reason why it hasn't started |
|||
==scontrol== |
|||
You can then show more info on one specific running job using the <code>scontrol</code> command, e.g for the job with ID 426 listed above: |
|||
<code> |
|||
scontrol show job 426 |
|||
</code> |
|||
displays detailed information for job with JobID 426 |
|||
<code> |
|||
scontrol show jobs |
|||
</code> |
|||
displays detailed information for all your jobs |
|||
<code> |
|||
scontrol write batch_script 426 - |
|||
</code> |
|||
display job script of a running job. The "-" is a special filename which means "write to the terminal". |
|||
== Monitoring a Started Job == |
|||
After a job has started, you can ssh from a login node to the node(s) the job is running on, using the node name from NODELIST, e.g. if your job runs on n4101: |
|||
<code>> ssh n4101 |
|||
</code> |
|||
== Job Examples == |
|||
Here you can find some example scripts for batch jobs. |
|||
=== Serial Programs === |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="slurm"> |
|||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
#SBATCH --partition=cpu |
|||
#SBATCH --ntasks=1 |
|||
#SBATCH --time=20:00:00 |
|||
#SBATCH --mem=3800mb |
|||
./my_serial_program |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
'''Notes:''' |
|||
* Jobs with "--mem" up to 500gb can run on all node types associated with the cpu partition. |
|||
=== Multi-threaded Programs === |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="slurm"> |
|||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
#SBATCH --partition=cpu |
|||
#SBATCH --nodes=1 |
|||
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 |
|||
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=32 |
|||
#SBATCH --time=01:30:00 |
|||
#SBATCH --mem=50gb |
|||
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=${SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK} |
|||
./my_multithreaded_program |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
'''Notes:''' |
|||
* Jobs with "--ntasks-per-node" up to 126 and "--mem" up to 500gb can run on all node types associated with the cpu partition. |
|||
* With "export OMP_NUM_THREADS=${SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK}" you can set the number of threads according to the number of resources requested. |
|||
=== MPI Programs === |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="slurm"> |
|||
#!/bin/bash |
|||
#SBATCH --partition=cpu |
|||
#SBATCH --nodes=2 |
|||
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=126 |
|||
#SBATCH --time=12:00:00 |
|||
module load mpi/openmpi # loads gcc |
|||
srun ./my_mpi_program |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
'''Notes:''' |
|||
* "--mem" requests the memory per node. The maximum is 500gb. |
|||
* The Compiler and MPI modules used for the compilation must be loaded before the start of the program. |
|||
* It is recommended to start MPI programs with 'srun'. |
|||
= Interactive Jobs = |
|||
Interactive jobs must NOT run on the login nodes, however resources for interactive jobs can be requested using srun. |
|||
The following examples requests an interactive session on 1 core for 2 hours. |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ salloc --partition=cpu --ntasks=1 --time=2:00:00</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
After execution of this command wait until the queueing system has granted you the requested resources. Once granted you will be automatically logged on the allocated compute node. |
|||
If you use applications or tools which provide a GUI, enable X-forwarding for your interactive session with. We suggest using VNC instead of X-forwarding: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ salloc --partition=cpu --ntasks=1 --time=2:00:00 --x11</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
Once the walltime limit has been reached you will be automatically logged out from the compute node. |
|||
= Job Monitoring = |
|||
== Information about submitted jobs == |
|||
For an overview of your submitted jobs use the command: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ squeue</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
To get detailed information about a specific job use the command: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ scontrol show job <jobid></syntaxhighlight> |
|||
'''Notes:'''<br> |
|||
A job start may be delayed for various reasons: |
|||
* (QOSMaxCpuPerUserLimit) - There is a limit to how many CPU cores a user can use at the same time. The job exceeds this limit. |
|||
* (QOSMaxGRESPerUser) - There is a limit to how many GPUs a user can use at the same time. The job exceeds this limit. |
|||
* (QOSMinGRES) - The job was submitted to a gpu partition without requesting a GPU. |
|||
* (launch failed requeued held) - The job has failed to start. You may be able to resume it using scontrol. Alternatively you can cancel it and submit it again. |
|||
For further reasons please refer to: https://slurm.schedmd.com/job_reason_codes.html |
|||
== Information about resource usage of running jobs == |
|||
You can monitor the resource usage of running jobs with the sstat command. For example: |
|||
<pre> |
|||
$ sstat --format=JobId,AveCPU,AveRSS,MaxRSS -j <jobid> |
|||
</pre> |
|||
This will show average CPU time, average and maximum memory consumption of all tasks in the running job. |
|||
'sstat -e' command shows a list of fields that can be specified with the '--format' option. |
|||
== Interactive access to running jobs == |
|||
It is also possible to attach an interactive shell to a running job with command: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ srun --jobid=<jobid> --overlap --pty /bin/bash</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
Commands like 'top' show you the most busy processes on the node. To exit 'top' type 'q'. |
|||
To monitor your GPU processes use the command 'nvidia-smi'. |
|||
== Job Feedback == |
|||
You get feedback on resource usage and job efficiency for completed jobs with the command: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
|||
$ seff <jobid> |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
Example Output: |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> |
|||
Job ID: 426 |
|||
Cluster: nemo |
|||
User/Group: fr_ab0123/fr_fr |
|||
State: COMPLETED (exit code 0) |
|||
Nodes: 2 |
|||
Cores per node: 190 |
|||
CPU Utilized: 19:13:22 |
|||
CPU Efficiency: 91.06% of 21:06:40 core-walltime |
|||
Job Wall-clock time: 00:03:20 |
|||
Memory Utilized: 15.48 GB |
|||
Memory Efficiency: 1.10% of 1.38 TB |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
'''bwForCluster Helix'''<br /> |
|||
Explanation: |
|||
You can directly access your storage space under ''/mnt/sds-hd/'' on all login and compute nodes. |
|||
* Nodes: Number of allocated nodes for the job. |
|||
* Cores per node: Number of physical cores per node allocated for the job. |
|||
* CPU Utilized: Sum of utilized core time. |
|||
* CPU Efficiency: 'CPU Utilized' with respect to core-walltime (= 'Nodes' x 'Cores per node' x 'Job Wall-clock time') in percent. |
|||
* Job Wall-clock time: runtime of the job. |
|||
* Memory Utilized: Sum of memory used. For multi node MPI jobs the sum is only correct when srun is used instead of mpirun. |
|||
* Memory Efficiency: 'Memory Utilized' with respect to total allocated memory for the job. |
|||
'''bwForCluster BinAC'''<br /> |
|||
= Accounting (not implemented) = |
|||
You can directly access your storage space under ''/mnt/sds-hd/'' on all login and compute nodes. The prerequisites are: |
|||
* The SV responsible has enabled the SV on BinAC once by writing to [mailto:sds-hd-support@urz.uni-heidelberg.de sds-hd-support@urz.uni-heidelberg.de] |
|||
* You have a valid kerberos ticket, which can be fetched with <code>kinit <userID></code> |
|||
'''Other'''<br /> |
|||
Jobs are billed for allocated CPU cores, memory and GPUs. |
|||
You can mount your SDS@hd SV on the cluster yourself by using [[Data_Transfer/Rclone#Usage_Rclone_Mount | Rclone mount]]. As transfer protocol you can use WebDAV or sftp. For a full overview please have a look at [[Data_Transfer/All_Data_Transfer_Routes | All Data Transfer Routes]]. |
|||
=== Access via Webbrowser (read-only) === |
|||
To see the accounting data of a specific job: |
|||
Visit [https://lsdf02-webdav.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/ lsdf02-webdav.urz.uni-heidelberg.de] and login with your SDS@hd username and service password. Here you can get an overview of the data in your "Speichervorhaben" and download single files. To be able to do more, like moving data, uploading new files, or downloading complete folders, a suitable client is needed as described above. |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ sacct -j <jobid> --format=user,jobid,account,nnodes,ncpus,time,elapsed,AllocTRES%50</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
== Best Practices == |
|||
To retrive the job history for a specific user for a certain time frame: |
|||
* '''Managing access rights with ACLs''' <br /> -> Please set ACLs either via the [https://www.urz.uni-heidelberg.de/de/service-katalog/desktop-und-arbeitsplatz/windows-terminalserver Windows terminal server] or via bwForCluster Helix. ACL changes won't work when used locally on a mounted directory. |
|||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">$ sacct -u <user> -S 2025-03-01 -E 2025-03-02 --format=user,jobid,account,nnodes,ncpus,time,elapsed,AllocTRES%50</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
* '''Multiuser environment''' -<br /> -> Use [[SDS@hd/Access/NFS|NFS]] |
|||
Revision as of 17:41, 14 May 2025
This page provides an overview on how to access data served by SDS@hd. To get an introduction to data transfer in general, see data transfer.
Prerequisites
- You need to be registered.
- You need to be in the belwue-Network. This means you have to use the VPN Service of your HomeOrganization, if you want to access SDS@hd from outside the bwHPC-Clusters (e.g. via eduroam or from your personal notebook).
Needed Information, independent of the chosen tool
- Username: Same as for the bwHPC Clusters
- Password: The Service Password that you set at bwServices in the registration step.
- SV-Acronym: Use the lower case version of the acronym for all access options.
- Hostname: The hostname depends on the chosen network protocol:
Recommended Setup
The following graphic shows the recommended way for accessing SDS@hd via Windows/Mac/Linux. The table provides an overview of the most important access options and links to the related pages.
If you have various use cases, it is recommended to use Rclone. You can copy, sync and mount with it. Thanks to its multithreading capability Rclone is a good fit for transferring big data.
For an overview of all connection possibilities, please have a look at all data transfer routes.
Figure 1: SDS@hd main transfer routes
| Use Case | Windows | Mac | Linux | Possible Bandwith | Firewall Ports | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rclone + <protocol> | copy, sync and mount, multithreading | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | depends on used protocol | depends on used protocol |
| SMB | mount as network drive in file explorer or usage via Rclone | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | up to 40 Gbit/sec | 139 (netbios), 135 (rpc), 445 (smb) |
| WebDAV | go to solution for restricted networks | [✓] | ✓ | ✓ | up to 100GBit/sec | 80 (http), 443 (https) |
| MobaXterm | Graphical User Interface (GUI) | ✓ | ☓ | ☓ | see sftp | see sftp |
| NFS | mount for multi-user environments | ☓ | ☓ | ✓ | up to 40 Gbit/sec | - |
| SSHFS | mount, needs stable internet connection | ☓ | ✓ | ✓ | see sftp | see sftp |
| SFTP | interactive shell, better usability when used together with Rclone | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | up to 40 Gbit/sec | 22 (ssh) |
Table 1: SDS@hd transfer routes
Access from a bwHPC Cluster
bwForCluster Helix
You can directly access your storage space under /mnt/sds-hd/ on all login and compute nodes.
bwForCluster BinAC
You can directly access your storage space under /mnt/sds-hd/ on all login and compute nodes. The prerequisites are:
- The SV responsible has enabled the SV on BinAC once by writing to sds-hd-support@urz.uni-heidelberg.de
- You have a valid kerberos ticket, which can be fetched with
kinit <userID>
Other
You can mount your SDS@hd SV on the cluster yourself by using Rclone mount. As transfer protocol you can use WebDAV or sftp. For a full overview please have a look at All Data Transfer Routes.
Access via Webbrowser (read-only)
Visit lsdf02-webdav.urz.uni-heidelberg.de and login with your SDS@hd username and service password. Here you can get an overview of the data in your "Speichervorhaben" and download single files. To be able to do more, like moving data, uploading new files, or downloading complete folders, a suitable client is needed as described above.
Best Practices
- Managing access rights with ACLs
-> Please set ACLs either via the Windows terminal server or via bwForCluster Helix. ACL changes won't work when used locally on a mounted directory. - Multiuser environment -
-> Use NFS